Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

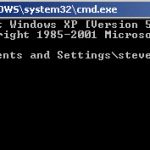
Windows has some very useful networking utilities that are accessed from a command line (cmd console).
On Windows 10 type cmd in the search box to open a command console.
The networking commands are mainly used for getting system information and troubleshooting networking problems.
Here we look at the 10 commands we use often.
The ping command is one of the most often used networking utilities for detecting devices on a network and for troubleshooting network problems.
When you ping a device you send that device a short message, which it then sends back (the echo).
The general format is ping hostname or ping IPaddress.
Example
ping www.google.com or ping 216.58.208.68
Another indispensable and frequently used utility that is used for finding network information about your local machine like IP addresses, DNS addresses etc
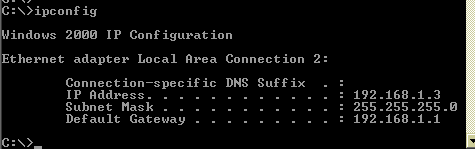
Basic Use: Finding Your IP Address and Default Gateway
Type the command ipconfig at the prompt.
The following is displayed
Ip config has a number of switches the most common are:
ipconfig /all – displays more information about the network setup on your systems including the MAC address.
ipconfig /release – release the current IP address
ipconfig /renew – renew IP address
ipconfig /? -shows help
ipconfig/flushdns – flush the dns cache
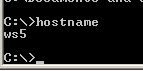
A very simple command that displays the host name of your machine. This is much quicker than going to the control panel>system route.
Another very simple command that shows the MAC address of your network interfaces
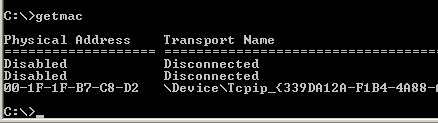
This is used for showing the address resolution cache. This command must be used with a command line switch arp -a is the most common.
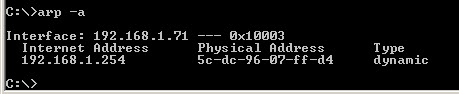
Type arp at the command line to see all available options.
Used for checking DNS record entries.
Diagnostic tool for troubleshooting netBIOS problems.
Used for managing users,service,shares etc
Used for displaying information about tcp and udp connections and ports.
View a list of running tasks using the tasklist command and kill them by name or processor ID using the taskKill command-